Agriculture of Gujarat
Gujarat has shown good progress in agriculture. The economy of Gujarat is largely dependent upon agriculture. More than 50 percent of the total available land is being used for agriculture.
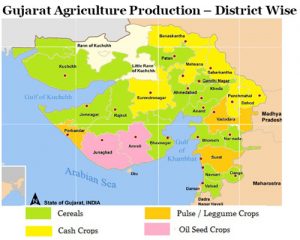
The main food crops are bajra, jowar, rice and wheat. Major commercial crops or cash crops are groundnut, tobacco and cotton, linseed, sugarcane, etc. Other important cash crops are isabgul (Psyllium husk), cumin, mangoes and bananas.
Agriculture of Gujarat is being modernized with the introduction of improvements, both technological and organizational.
- High yielding varieties of seeds are being used.
- Chemical fertilizers are applied and
- Irrigation has been improved by utilizing properly both ground water and surface water resources of the State.
- The diversified cropping pattern of Gujarat is amply supported by irrigation.
- Cold-storage, logistics and improved infrastructure is being developed.
- The agricultural research institutes give further boost for sustained output.
As a result, productions of different crops have been steadily increasing. Cooperative farming has given a major boost to the agricultural and economic growth of Gujarat. Amul daily is world’s largest milk dairy program.
Gujarat is passing through a growth phase in the field of agriculture. High yielding varieties (HYV) of seeds, are being used. Chemical fertilizers are applied and irrigation is improved both ground and surface water.
During the recent years, Gujarat has witnessed significant improvement in the field of agriculture. The agricultural growth rate was over 9% during the period 2000-2010, as against a growth rate of around 3% during the 1990s. During the period between 2000 and 2008, the growth rate of wheat production stood at 28%.
Gujarat now ranks first in the production of groundnut and second in the production of tobacco. Other cash crops of Gujarat are Isabgul, Cumin, Mangoes and Bananas.
Gujarat ranks second to Andhra Pradesh in tobacco production. It is concentrated in the alluvial soil of Kheda district. Castor, sesamum, vegetables, and fruits, grow well on a fertile goradu soil (partly loss) of the plains.
In Kutch, north-west Kathiawar and north Gujarat where rainfall is very little and uncertain for agriculture, goats, sheep and cattle are reared. At Anand (Kheda district) there is a modern dairy industry run on co-operative basis. Coastal fishing is not as important as the Gujaratis are mostly vegetarians.
Gujarat is a maritime state. The state is drained by the river Narmada, Tapti, Mahe, and Sabarmati. The soil of this state is the mixture of three Black soils, Sandy soil and Alluvium soil.
So, the main agricultural crops are bajra, jawar, rice, and wheat. Major commercial crops of cash crops are cotton, tobacco and groundnut, linseed, sugar-cane, etc. Groundnuts cover the maximum acreage among all crops. Cotton stands second. The food crops are widely defused. Fruits and vegetables also contributes towards agriculture.
Groundnut is mostly concentrated in the peninsular Gujarat with light, and gribble soil. Tobacco is concerned in Kheda and Vadodra. Cotton is raised in Gujarat Plain. Here, rainfall is in between 60 to 100 cm. Cash crops play an important role in the economy of the state.
Besides climatic and other geographical factors, the recent success of agriculture in Gujarat is mainly attributed to the efforts of state-run institutions and introduction of HYV seeds, improved irrigation methods, etc. The various state promoted agricultural universities work towards implementation of new technologies. The improved marketing, warehousing, and cold-storage infrastructures ensurer marketability, sustainability and efficacy of food products
Gujarat became the first state to implement Agro-Solar Policy
Under this, farmers are roped in to tap energy from sun which will also help them earn additional income from power generation companies.
The Gujarat Energy Research and Management Institute (GERMI) manage the projects under this policy. The farmer are able to produce energy locally without depending on the state and can also create a surplus.The farmers get a chance to supplement their income by installing these Solar Photo Volatic (SPV) panels and selling the surplus to other private or government owned power generation companies.
Some other successful solar projects in Gujarat State has Asia’s largest solar power plant in Charanka village in Patan district which is built on a 2,000-hectare land. In January 2015, the first canal-top solar power plant (10 MW solar capacity) was inaugurated by UN Secretary General Ban-Ki Moon on Narmada canal in Vadodara.
Overall, the farmers now get a supplementary income as revenue are shared by the power generation companies. Besides, the companies get good space for electricity generation.
GPSC Notes brings Prelims and Mains programs for GPSC Prelims and GPSC Mains Exam preparation. Various Programs initiated by GPSC Notes are as follows:-
- GPSC Mains 2024 Tests and Notes Program
- GPSC Prelims Exam 2024- Test Series and Notes Program
- GPSC Prelims and Mains 2024 Tests Series and Notes Program
- GPSC Detailed Complete Prelims Notes