Gujrat Human Development Index
Human Development Index (HDI)
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a summary measure of average achievement in key dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, being knowledgeable and have a decent standard of living. The HDI is the geometric mean of normalized indices for each of the three dimensions.
The index was developed by Mahbub-ul-Haque along with Amartya Sen which is used by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in their annual report since 1990.
Its goal was to place people at the centre of the development process in terms of economic debate, policy and advocacy. This report ranks the countries on the basis of the Human
Development Index.Human Development Index for Indian States have also been calculated depending on the data collected from various sources for Indian states.
It measures the average achievements in a country in three basic dimensions of human development:
- A long and healthy life
- Access to knowledge
- Decent standard of living
Health (A long and healthy life)
The estimates of life expectancy for 16 major states are obtained from SRS Based Abridged Life Tables 2002-2006. The estimates of inequality have also been derived from the SRS Based Abridged Life Tables, which also provides a profile of mortality across age-intervals for the Indian states.
Education (Access to knowledge)
The mean years of schooling of the adult population (aged 25 years and above) are estimated using the NSS data on educational status and training in India. The same data source is used to obtain estimate of Atkinson inequality in levels of education. Estimates of school life expectancy are made based on the NSS unit record data on education in India
Income (Decent standard of living)
The HDI uses the estimate of Gross National Income per capita (PPP US$) for India from the HDR 2010. Per capita income estimates for states are computed using the National Sample Survey (NSS) estimates of per capita personal consumer expenditure for the year 2004-05 assuming that size distribution of income distribution across states is the same as that of NSS consumer expenditure distribution.
HDI used estimates of Atkinson measure of inequality based on the NSS unit record data on per capita consumer expenditure distribution for the year 2004-05 as proxy for corresponding inequality estimate of income.
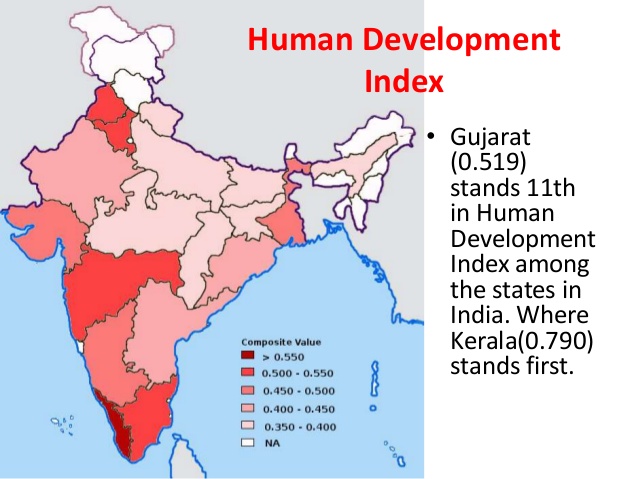
Gujrat Human Development Index
HDI value for state of Gujarat in 2015 was 0.616, which places the state in middle income state. It ranks 11th in the Indian states.
Performance of the Social sectors as linked with the wellbeing of the people becomes key to State Human Development.
Gujrat Human Development Focus
The State aims to become a model State on all fronts of Human Development. Every single person in the State, irrespective of gender, caste or creed would:
- Be literate and healthy
- Have shelter and clean environment
- Have drinking water and sanitation
- Be gainfully employed
- Be able to live without fear
- Have equal opportunities
The strategy of 12th Five Year Plan (2012-17), addressed the economic wellbeing of the people with Human Development Approach. The State Government has given the highest priority for the development of Social Sectors which have direct impact on Human Development by allocating nearly about 47.09 percent of the total outlay to Social Sectors in the year 2016-17.
To address specific
issues of the under privileged societies and areas, State Government launched “Flagship Programmes” like Sagarkhedu Sarvangi Vikas Yojana, Vanbandhu Kalyan Yojana, Garib Samruddhi Yojana and 49 Developing Talukas. Besides this various “Mission Mode Programmes” like Kanya Kelavani, Gunotsav, Krishi Mahotsav, Nirmal Gujarat, Skill Development, Nirogi Bal, Bal Sakha Yojana, Balbhog Yojana, Mamata Abhiyan, e-Mamta, MA, Mukhyamantri Amrutum Vatsalya Yojana, e-MPOWER, Chiranjeevi Yojana, Kaushalya Vardhan Kendra, Mukhyamantri Yuva Swavalamban Yojana etc., are also being implemented to improve Human Development Index.The Government of Gujarat is endeavoring to achieve the objectives of total literacy by Strengthening various programmes/ schemes of Primary Education, Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Higher Education and Technical Education. The State Government has started various programmes like”Vidya Deep Insurance”, “Vidya Laxmi Bond”, “Distribution of Cost free Text Book”, “Kanya Kelavani Mahotsav” and “Gunotsav Programme”, “Free bicycles to Girls”, “CM Scholarship Scheme”etc. to improve quality of education.
The State Government has established an autonomous body “Gujarat Social Infrastructure Development Society (GSIDS)” to improve the living standard of the people at large. The Society has Governing Body consisting of 10 members. Principal Secretary (Planning), General Administration Department is the Chairperson of GSIDS.
District Human Development Report (DHDR)
GSIDS has undertaken the preparation of District Human development report for all 33 districts in the state.
The District Human Development Report (DHDR) for 8 Districts; i.e. Banaskantha, Sabarkantha, Jamnagar, Dang, Surendranagar, Bharuch, Tapi and Kheda District DHDR reports have been published during the year 2015-16. The DHDR for 10 Districts; i.e. Porbandar, Ahmedabad, Narmada, Navsari, Mahesana, Patan, Kachchh, Surat, Junagadh and Panchmahal District DHDR reports are published during the year 2016-17.
Further DHDR for eight districts; i.e. Vadodara, Dahod, Rajkot, Bhvanagar, Amreli, Gandhinagar, Anand and Valsad District DHDR are planned to be published by the end of the year 2016-17. The District Human Development Report for newly created seven districts are under preparation and will be finalized during the year 2017-18.
Human Development towards Bridging Inequalities (HDBI)
Since 2013, Government of Gujarat (GoG) has been involved with a project initiated by erstwhile Planning Commission-UNDP (presently NITI Aayog), called ‘Human Development: Towards Bridging Inequalities’ (HDBI). A project steering committee under chairmanship of Hon. Principal Secretary (Planning) has been formed.
Moving from DHDR to DHDPs (District Human Development Plans)
On the basis of gap analysis from the DHDRs, focus areas are being identified. Accordingly, District Human Development Plan (DHDP) are being prepared. DHDPs have been finalised for Bharuch, Kheda, Narmada, Navsari, Sabarkantha, Tapi, Mahesana and DHDPs will be finalised by March-2017 for the remaining 26 districts.
In order to encourage institutions to develop and incorporate courses on Human Development in academia, three workshops/seminars were organized at Sardar Patel University-Anand, NICMGandhinagar, and CHARUSAT-Changa in collaboration with Higher and technical Education Department.
District Human Development
District Human Development Profile covers talukawise status of social sectors with 100 indicators comprising Demographics, Health, Education, Livelihood, etc. GSIDS has prepared District Human Development Profile for all the 33 districts of the State.
Taluka Development Plan (TDP)
To encourage the Taluka Centric Approach as well as the bottom of planning process in decentralized district planning, Gujarat has initially decided to prepare Taluka Development Plan (TDP) for one Taluka (33 Talukas) from each district.
Impact Evaluation of Flagship Scheme of Developing Talukas
Impact Evaluation of flagship scheme of Developing Talukas has been undertaken, in order to assess the utilization of funds and achievement of progress in the identified indicators in the respective talukas.
Empanelment of Subject Specialist/ Consultant
Government of Gujarat has empanelled 22 Subject Specialists/ Consultants to initiate Third Party Evaluation studies by various Departments to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of various government schemes and programs.
GPSC Notes brings Prelims and Mains programs for GPSC Prelims and GPSC Mains Exam preparation. Various Programs initiated by GPSC Notes are as follows:-
- GPSC Mains 2025 Tests and Notes Program
- GPSC Prelims Exam 2025- Test Series and Notes Program
- GPSC Prelims and Mains 2025 Tests Series and Notes Program
- GPSC Detailed Complete Prelims Notes