Gujarat: Population
- As per Census 2011, Gujarat covered 26 Districts, 225 Talukas, 348 Towns (195 Statutory Towns and 153 Census Towns) and 18225 Villages (including Uninhabited). There is an increase of 106 towns consisting of 27 statutory towns and 79 census towns as compared to Census 2001.
- By bifurcating existing districts, Government of Gujarat has formed 7 new districts and 23 talukas on 13th August, 2013. Accordingly, from 15th August, 2013, there are total 33 districts and 250 talukas in Gujarat State.
Population: The population of India at 0.00 Hrs. as on 1st March 2011 is 121.09 crore comprising 62.33 crore males and 58.76 crore females. The population of Gujarat at the same date and time is 6.04 crore comprising 3.15 crore males and 2.89 crore females. Of this, the rural population stands at 3.47 crore and the urban population 2.57 crore. The rural population has increased by 29.54 lakh and the urban population by 68.15 lakh in the last decade.
- Gujarat stands at 10th rank amongst the States in the country in respect of population and at 14th rank (excluding UTs) in population density. In terms of percentage, Gujarat accounts 5.97% of the area of India and 4.99% of the population of India.
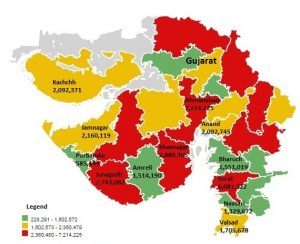
- The three districts viz. Ahmedabad, Surat and Vadodara are contributing 29% of the population of Gujarat. Nearly 50% of the State’s population resides in the 7 districts viz. Ahmadabad, Surat, Vadodara, Rajkot, Banas Kantha, Bhavnagar and Junagadh.
- Ahmedabad is the most populous district in the state recorded a population of 72.14 lakh followed by Surat district with a population of 60.81 lakh and The Dangs district has the minimum population of 2.28 lakh.
- Age groupwise distribution : Age is one of the core parameters in population census. Distribution of population by age is an essential perquisite for dissemination of census results and for population projection. Persons in age-group 10-19 years (Adolescent) have decreased by 1.55% in census 2011 (19.88%) as compared to census 2001 (21.43%). Persons in age-group 15-24 years (Youth) decreased by 0.51% in census 2011 (19.27%) as compared to census 2001 (19.78%). Persons in age-group 15-59 years (working age) have also decreased by 2.63% in census 2011 (60.19%) as compared to census 2001(62.82%).
Whereas, persons in age-group 60 years and above have increased by 1.01% in census 2011 (7.92%) as compared to census 2001 (6.91%).
- Urban – Rural Proportion : In percentage 1.12 terms, the rural population formed 57.4% of the total population (decrease of 5.2 % during the decade) and the urban population is 42.6% (increase of 5.2 % during the decade).
- Decennial Growth Rate : Population of Gujarat was 5.07 crore in the beginning of the 21st Century. As per Census 2011, Gujarat has population of 6.04 crore persons showing a decadal growth rate of 19.3% as compared to all India growth rate of 17.7%. The growth rate of population in rural and urban areas was 9.3% and 36.0% respectively.
- The growth rate of 2001-2011 for Gujarat state is decreased by 3.4% than the corresponding rate of growth during 19912001 which was at 22.7%. Though the overall growth rate of Gujarat state is decreased during 2001-2011, in 3 districts viz. Kachchh, Amreli and Dohad, the growth rate has increase as compared to 1991-2001 period. In Narmada district.
- There is a slight increase in growth rate as compared to 1991-2001. Surat district is having the highest decennial growth rate of 42.2% during 2001-2011. During 1991-2001 also, Surat district topped the districts in respect of growth rate with 54.3%. Besides Surat district, there are 7 other districts, which have higher growth rates than the State growth rate in Census 2011. They are Kachchh (32.2%), Dohad (30.0%), Banaskantha (24.6%), Ahmedabad (22.4%), The Dangs (22.3%), Valsad (20.9%) and Rajkot (20.0%). However, 12 districts have recorded very low growth rate which are Navsari (8.2%), Amreli (8.6%), Porbandar (9.1%), Mahesana (10.3%), Junagadh (12.0%), Tapi (12.1%), Gandhinagar (12.5%), Anand (12.7%), Kheda (12.9%), Bharuch (13.2%), Jamnagar (13.4%) and Patan (13.6%).
- Sex Ratio : The Sex Ratio is defined as number of Female per 1000 Male Population.
- The Sex Ratio in the country was 933 in 2001 which has risen by 10 points to 943 in 2011. The increase in rural areas has been 3 points i.e. from 946 to 949. The increase in urban areas has been 29 points i.e. from 900 to 929.
- Child Population (0-6 years) : As per Census 2011, out of the child population of 77.77 lakh in the age group of 0-6 years in the state, the rural child population is 48.25 lakh and urban child population is 29.52 lakh. The child population has increased to 77.77 lakh in 2011 from 75.32 lakh in 2001, registering a growth of 3.25% (Chart-5).
- Child Sex Ratio (0-6 years) : At national level, Census 2011 shows a decrease of 9 points in child sex ratio in the age group of 0-6 years and has fallen from 927 in 2001 to 918 in 2011. In rural areas, there is a decrease of 11 points (934-923) and in urban areas it is 1 point (906-905) over the decade 2001-2011. The child sex ratio at all India level has decline shown in all the last five decades.
- In Gujarat, the child sex ratio has increased from 883 in 2001 to 890 in 2011. In rural areas it was 906 in 2001 and increased to 914 in 2011, while in urban areas it has increased considerably by 15 points to 852 in 2011 from 837 in 2001. For the first time in the last five decades, Gujarat has recorded an improvement in child sex ratio in the decade from 2001 to 2011.
- Literacy Rate : In census concept, a person is treated as literate if one can read and write with understanding in any language. However, the children below the age of 7 years have not been treated as literate, even if they may be able to read and write with understanding.
- The literacy rate of Gujarat as per the population census 2011 is 78.0%. In rural areas the literacy rate is 71.7% and in urban areas it is 86.3%. The decadal increase works out to 8.9 points. In rural and urban areas it works out to 10.4 points and 4.5 points respectively. The male literacy rate is 85.8% (Rural 81.6%, Urban 91.0%) which is higher than the female literacy rate of 69.7% (Rural 61.4%, Urban 81.0%). The increase in female literacy rate is significantly higher in all areas i.e. total (11.9 points), rural (13.6 points) and urban (6.5 points) in comparison to increase in corresponding male literacy rates of total (6.1 points), rural (7.5 points) and urban (2.7 points) over the decade. It is significant to note that the gap in literacy rate among males and females has reduced to 16.1 point in the state from 21.9 points in 2001. The gap is 20.2 points in rural areas and 10.0 points in urban areas . Amongst all the districts, Surat district stands at 1st rank in literacy with 85.5% followed by Ahmedabad (85.3%), Anand (84.4%). On the other hand from bottom side, Dohad district stands at 1st rank in literacy with 58.8% followed by Banaskantha district (65.3%) and Tapi district (68.3%) and so on. Sex wise literacy rate shows that the Gandhinagar district occupies the 1st rank (92.0%)
- GPSC Mains 2025 Tests and Notes Program
- GPSC Prelims Exam 2025- Test Series and Notes Program
- GPSC Prelims and Mains 2025 Tests Series and Notes Program
- GPSC Detailed Complete Prelims Notes
